«I kept my faith even when I said, “I am greatly afflicted”» (Ps 116:10): life in old age and at times of suffering
46. With regard to the last moments of life too, it would be anachronistic to expect biblical revelation to make express reference to present-day issues concerning respect for elderly and sick persons, or to condemn explicitly attempts to hasten their end by force. The cultural and religious context of the Bible is in no way touched by such temptations; indeed, in that context the wisdom and experience of the elderly are recognized as a unique source of enrichment for the family and for society.
Old age is characterized by dignity and surrounded with reverence (cf. 2 Mac 6:23). The just man does not seek to be delivered from old age and its burden; on the contrary his prayer is this: "You, O Lord, are my hope, my trust, O Lord, from my youth ... so even to old age and grey hairs, O God, do not forsake me, till I proclaim your might to all the generations to come" (Ps 71:5, 18). The ideal of the Messianic age is presented as a time when "no more shall there be ... an old man who does not fill out his days" (Is 65:20).
In old age, how should one face the inevitable decline of life? How should one act in the face of death? The believer knows that his life is in the hands of God: "You, O Lord, hold my lot" (cf. Ps 16:5), and he accepts from God the need to die: "This is the decree from the Lord for all flesh, and how can you reject the good pleasure of the Most High?" (Sir 41:3-4). Man is not the master of life, nor is he the master of death. In life and in death, he has to entrust himself completely to the "good pleasure of the Most High", to his loving plan.
In moments of sickness too, man is called to have the same trust in the Lord and to renew his fundamental faith in the One who "heals all your diseases" (cf. Ps 103:3). When every hope of good health seems to fade before a person's eyes-so as to make him cry out: "My days are like an evening shadow; I wither away like grass" (Ps 102:11)- even then the believer is sustained by an unshakable faith in God's life-giving power. Illness does not drive such a person to despair and to seek death, but makes him cry out in hope: "I kept my faith, even when I said, ?I am greatly afflicted' " (Ps 116:10); "O Lord my God, I cried to you for help, and you have healed me. O Lord, you have brought up my soul from Sheol, restored me to life from among those gone down to the pit" (Ps 30:2-3).
47. The mission of Jesus, with the many healings he performed, shows God's great concern even for man's bodily life. Jesus, as "the physician of the body and of the spirit",37 was sent by the Father to proclaim the good news to the poor and to heal the brokenhearted (cf. Lk 4:18; Is 61:1). Later, when he sends his disciples into the world, he gives them a mission, a mission in which healing the sick goes hand in hand with the proclamation of the Gospel: "And preach as you go, saying, ?The kingdom of heaven is at hand'. Heal the sick, raise the dead, cleanse lepers, cast out demons" (Mt 10:7-8; cf. Mk 6:13; 16:18).
Certainly the life of the body in its earthly state is not an absolute good for the believer, especially as he may be asked to give up his life for a greater good. As Jesus says: "Whoever would save his life will lose it; and whoever loses his life for my sake and the gospel's will save it" (Mk 8:35). The New Testament gives many different examples of this. Jesus does not hesitate to sacrifice himself and he freely makes of his life an offering to the Father (cf. Jn 10:17) and to those who belong to him (cf. Jn 10:15). The death of John the Baptist, precursor of the Saviour, also testifies that earthly existence is not an absolute good; what is more important is remaining faithful to the word of the Lord even at the risk of one's life (cf. Mk 6:17-29). Stephen, losing his earthly life because of his faithful witness to the Lord's Resurrection, follows in the Master's footsteps and meets those who are stoning him with words of forgiveness (cf. Acts 7:59-60), thus becoming the first of a countless host of martyrs whom the Church has venerated since the very beginning.
No one, however, can arbitrarily choose whether to live or die; the absolute master of such a decision is the Creator alone, in whom "we live and move and have our being" (Acts 17:28).
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
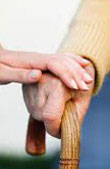
94. Special attention must be given to the elderly. While in some cultures older people remain a part of the family with an important and active role, in others the elderly are regarded as a useless burden and are left to themselves. Here the temptation to resort to euthanasia can more easily arise.
Neglect of the elderly or their outright rejection are intolerable. Their presence in the family, or at least their closeness to the family in cases where limited living space or other reasons make this impossible, is of fundamental importance in creating a climate of mutual interaction and enriching communication between the different age-groups. It is therefore important to preserve, or to re-establish where it has been lost, a sort of "covenant" between generations. In this way parents, in their later years, can receive from their children the acceptance and solidarity which they themselves gave to their children when they brought them into the world. This is required by obedience to the divine commandment to honour one's father and mother (cf. Ex 20:12; Lev 19:3). But there is more. The elderly are not only to be considered the object of our concern, closeness and service. They themselves have a valuable contribution to make to the Gospel of life. Thanks to the rich treasury of experiences they have acquired through the years, the elderly can and must be sources of wisdom and witnesses of hope and love.
Although it is true that "the future of humanity passes by way of the family",122 it must be admitted that modern social, economic and cultural conditions make the family's task of serving life more difficult and demanding. In order to fulfil its vocation as the "sanctuary of life", as the cell of a society which loves and welcomes life, the family urgently needs to be helped and supported. Communities and States must guarantee all the support, including economic support, which families need in order to meet their problems in a truly human way. For her part, the Church must untiringly promote a plan of pastoral care for families, capable of making every family rediscover and live with joy and courage its mission to further the Gospel of life.
Evangelium Vitae